- Cellulose
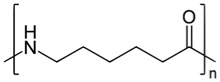
- Nylon 6
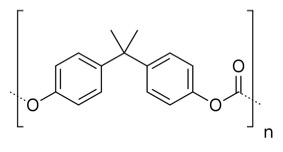
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Polycaprolactone (PCL)
- Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)
- Polyester (PET)
- Polyethersulfone (PES)
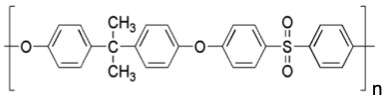
- Polysulfone (PSU)
- Polyethylene (LDPE)
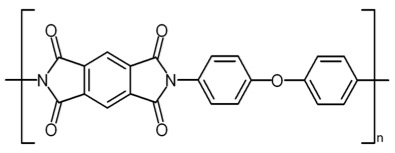
- Polyimide (PI)
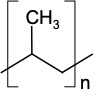
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Polystyrene (PS)
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
- Polyurethane (PU)
- Polyvinyl fluoride (PVF)
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.44 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 58 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 220 |
| Refractive Index | 1.48 |
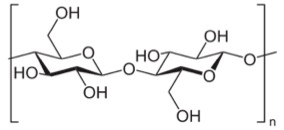
The vibration lines in 1800 - 1600 cm-1 region are
usually asigned to C=O, C=N or C=C bonds. Chemical structure of
"ideal" cellulose does not contain any of these groups and, in
literature, 1650 cm-1 peak is interpreted as adsorbed
water [1], which is possible as cellulose is hydrophilic. C=O
bonds formed as defects during cellulose synthesis can also
provide some contribution to the intensity of 1650 cm-1
peak.
[1] X. Guo, L. Liu, J. Wu, J. Fan, Y. Wu.
Qualitatively and quantitatively characterizing water adsorption
of a cellulose nanofiber film using micro-FTIR spectroscopy.
RSC Adv, 8(2018)4214-4220.
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.13 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 72.4 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 47 |
| Refractive Index | 1.53 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.20-1.22 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 2.0-2.4 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 147 |
| Refractive Index | 1.58 |
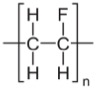
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.15 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 1.2 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | - 60 |
| Refractive Index | 1.48 |
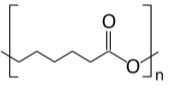
| Density, g/cm3 | 0.97 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 0.4-0.9 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | - 125 |
| Refractive Index | 1.40 |
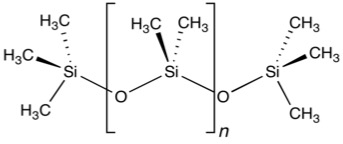
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.38 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 2.8-3.1 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 67-81 |
| Refractive Index | 1.58 |
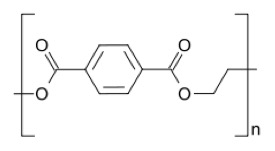
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.37 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 2.4-2.9 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 203-225 |
| Refractive Index | 1.65 |
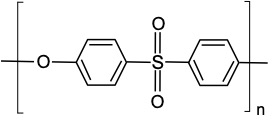
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.24 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 0.4 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 190-230 |
| Refractive Index | 1.63 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 0.91-0.96 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 0.1-0.5 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 100 |
| Refractive Index | 1.51-1.54 |
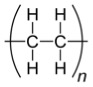
Although chemical structure of "ideal" polyethylene does not
contain C=O bonds, weak vibration lines corresponding to these
bonds can be observed in FTIR-ATR spectrum at 1735 cm-1
due to photooxidation or synthesis defects [2].
The vibration lines in 3000 - 2800 cm -1 region
correspond to assymetrical/symmetrical stretch, while the
vibration lines in 1490 - 1300 cm -1 and 760 - 700 cm
-1 regions are assigned to bend and rocking,
respectively.
[2] L. Chen, T.D. Huan, R. Ramprasad.
Electronic Structure of Polyethylene: Role of Chemical,
Morphological and Interfacial Complexity.
Sci Rep, 7(2017)6128.
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.45 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 2.5 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 350 |
| Refractive Index | 1.70 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 0.86-0.95 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 1.3-1.8 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 100 |
| Refractive Index | 1.49-1.52 |
| Density, g/cm3 | 0.96-1.05 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 3.0-3.6 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 100 |
| Refractive Index | 1.60 |
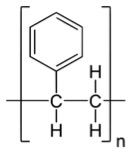
| Density, g/cm3 | 2.2 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 0.5 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 115 |
| Refractive Index | 1.38 |
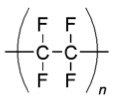
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.01-1.26 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | (0.9-4.5)x10-3 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | -65 |
| Refractive Index | 1.65 |
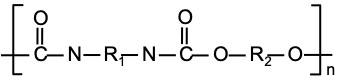
| Density, g/cm3 | 1.45 |
|---|---|
| Young's Modulus, GPa | 2.1 |
| Glass Transition Temperature, oC | 53 |
| Refractive Index | 1.46 |